Anatomy:
The eyelids are movable tissue situated in front of the eyeball. It protects the eyes from injuries & excess light. They also helps in spreading and drainage of tears.
If the eyes are open, the upper lid covers about one-sixth of the cornea and lower lid just touches the limbus.
The two lids meet eachother at medial and lateral angles called inner and outer canthi.
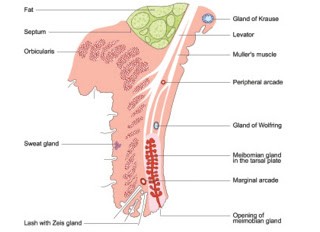
Layers of Eyelids:
1. Cutaneous layer (skin)
2. Areolar layer (loose areolar tissue)
3. Muscular layer (orbicularis oculi)
4. Submuscular areolar tissue
5. Fibrous layer (tarsal plate & septum orbitals.
6. Layer of smooth muscle (Muller's muscle)
7.conjunctival layer.
Glands of Eyelids:
1. Meibomian glands
2. Glands of Zeis
3. Glands of Moli
4. Glands of Wolfring
Blood supply:
Arteries: Marginal arterial arcades & superior arterial arcade.
Veins: post-tarsal vein drains into ophthalmic vein & pre-tarsal vein drains into subcutaneous veins.
Lymphatics: pre-tarsal and post-tarsal lymphatics drain into pre-auricular and submandibular lymph nodes respectively.
Nerve supply:
Motor nerves: Facial,occulomotor and sympathetic fibres.
Sensory nerves: Trigeminal Nerve and supratrochlear nerve for upper lid. Infraorbital nerve for lower lid.
Eyelash Disorders:
1.Trichiasis:
Inward misdirection of cilia (which rub against the eyeball) with normal position of the lid margin.
Pseudotrichiasis : The inward turning of lashes along with lid margin.
Causes : Cicatricial trachoma, ulcerative blepharitis,healed membraneous conjunctivitis,burns and operative scar on the lid margins.
Clinical features:
Symptoms:
- foreign body sensation
- photophobia
- Irritation ypain and lacrimation.
Signs:
- Misdirected cilia,one or more touching the cornea
- Reflex blepharospasm and photophobia
- Conjunctival congestion.
Complications:
- Recurrent corneal abrasions
- Superficial corneal opacities
- Corneal vascular risation
- Non healing corneal ulcer.
Treatment:
- Epilation
- Electrolysis
- Cryoepilation
- Surgical Correction
2.Distichiasis:
1.Congenital Distichiasis:
Extra row of cilia occupies the position of Meibomian glands which open into their follicles as ordinary sebaceous glands.
These cilia are usually directed backwards.
Treatment:
- Electroepilation
- Cryoepilation
2. Acquired Distichiasis:
When Meibomian glands are transformed into hair follicles due to metaplasia.
Causes:
Cicatrising conjunctivitis due to chemical injury,steven-johnson syndrome, ocular cicatricial pemphegoid.
3.Madarosis:
Partial or complete loss of eyelashes.
Local causes: chronic blepharitis, cicatrizing conjunctivitis, complications of cryotherapy, radiotherapy or surgery done for any eyelid lesions.
Systemic causes: alopecia, psoriasis, hypothyroidism and leprosy.
4.Trichomegaly:
Excessive growth of eyelashes.
Causes:
Congenital,familial,drug induced (topical prostaglandin analogue, phenytoin and cyclosporine), malnutrition, hypothyroidism,porphyria, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
5.Poliosis:
Greying if eyelashes and eyebrows.
Occular causes: chronic anterior blepharitis, systemic ophthalmitis and idiopathic uveitis.
Systemic conditions: vogt konyangi-harada syndrome,waardenburg syndrome,vitiligo,Marfan syndrome,tuberous sclerosis.
Anomalies in the position of lid margins:
1.Entropion:
Inward rolling and rotation of the lid margins towards globe.
Types of Entropion:
- Congenital Entropion
- Cicatricial Entropion
- Senile Entropion
- Mechanical Entropion
Clinical features:
Symptoms:
- Occurs due to rubbing of cilia against the cornea and conjunctiva.
- foreign body sensation
- irritation
- lacrimation
- photophobia
Signs:
- Interning of lid margins
- Signs of causative disease(scarring & horizontal lid laxity)
- Signs of complication( corneal abrasion, corneal opacities, corneal vascularization & corneal ulceration).
Treatment:
1. Congenital Entropion:
Resolve with time sometimes need of Birth procedure.
2. Cicatricial Entropion:
Treated by plastic operations,
- Anterior lamellar resection
- Tarsal wedge resection
- Transposition of tarsoconjunctival wedge.
- Posterior lamellar graft
3. Senile Entropion:
Surgical techniques are as below,
- Transverse everting suture
- Wies operation
- Plication of lower lid retractors
- Quickert procedure
2.Ectropion:
Out rolling or outward turning of the lid margins is called ectropion.
Types of Ectropion:
a) Congenital Ectropion
b) Involutional Ectropion (only lower lids)
c) Cicatricial Ectropion
d) Paralytic Ectropion
e) Mechanical Entropion
Clinical features:
Symptoms:
- Epiphora
- irritation, discomfort and photophobia.
Signs:
- lid margins is outrolled
- signs of the etiological condition ( skin scars, seventh nerve palsy)
- horizontal lid laxity
- medial canthal tendon laxity
- lateral canthal tendon laxity.
Complications:
- Dryness and thickening of conjunctiva and corneal ulceration
- Eczema and dermatitis
Treatment:
1.congenital ectropion:
Mild ectropion requires no treatment
2.Involutional ectropion:
- Medial conjunctivoplasty
- Horizontal lid shortening
- Byron Smith's modified operation
- Lateral tarsal strip technique
3.Paralytic ectropion:
Resolves spontaneously, sometimes permanent measures include Horizontal lid tightening and Palpebral sling operation can be done.
4. Cicatricial Ectropion:
- VY operation
- Z plasty( Elsching's operation)
- Excision of scar tissue & full thickness skin grafting.
5. Mechanical Entropion:
It is corrected by treating the underlying cause.
3.Symblepharon:
Lids become adherent with the eyeball,as a result of adhesions between the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva.
Etiology:
It results from healing of the kissing raw surfaces upon the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva.
Common causes are burns,Conjunctival injuries & ulceration,pemphigus and Stevens Johnson syndrome.
Clinical features:
- Restriction of occular movements
- Diplopia
- Lagophthalmos
- Cosmetic disfigurement
Types of Symbleopharon:
(depending on extent of adhesions)
1. Anterior Symbleopharon
2. Posterior Symbleopharon
3. Total Symbleopharon
Complications:
Thickening,dryness and keratinization of conjunctiva.
Treatment:
a) Prophylaxis:
- Sweeping a glass rod coated with lubricant around the fornices several times a day.
- Therapeutic soft contact lens of larger size,also helps in preventing the adhesions.
b) Curative treatment:
Symbleopharectomy,raw surface created by
- Mobilising the surrounding conjunctiva
- Conjunctival or buccal mucosal graft
- Amniotic membrane transplantation.
4. Ankyloblepharon:
Adhesions between margins of the upper and lower lids.
Etiology:
- congenital
- acquired adhesions
(after healing of chemical burns,thermal burns,ulcers & wounds of the lid margins)
It is usually associated with Symbleopharon.
Treatment:
- Excision of adhesions between the lids
- If adhesions extend to the angels, epithelial grafts are used.
5.Blepharophimosis:
The extent of the palpebral fissure is decreased
Etiology:
Congenital or Acquired, by the formation of vertical skin fold at the lateral canthus.
Treatment:
Cathoplasty is performed. Sometimes treatment is not required.
6. Lagophthalmos:
Inability to close the eyelids voluntarily.
Etiology:
- paralysis of orbicularis oculi
- Symbleopharon
- Cicatricial contraction of the lids
- Ectropion
- Proptosis
- Nocturnal Lagophthalmos.
Clinical features:
Incomplete closure of the palpebral aperture.
Complications:
- Conjunctival & corneal Xerosis
- exposure keratitis
Treatment:
- Artificial tear drops
- Soft bandage contact lens
- Tarsorrhapy
- treatment of Lagophthalmos.
7.Blepharospasm:
Involuntary, sustained and forceful closure of the eyelids.
Etiology:
1. Spontaneous blepharospasm:
Idiopathic and rare condition.
2. Reflex blepharospasm:
Due to reflex sensory stimulation through branches of 5th nerve.
Clinical features:
- persistent Epiphora
- oedema of the lids
- spastic Entropion
- blepharophlmosis
Treatment:
For spontaneous blepharospasm:
- Botulinum toxins, injected subcutaneously over the orbicularis muscle blocks the neuromuscular junction & relieves spasm.
- Facial denervation
For reflex blepharospasm:
- treatment of causative factors
- treatment of associated complications.




























Social Plugin